Inventory is a crucial part of any business and the reorder point is an important part of managing that inventory. The reorder point is the point at which a business needs to reorder inventory to keep up with customer demand. An effective reorder point ensures that your business keeps flowing— it helps you fulfill orders quickly, protects your margins, and keeps customers happy. Let’s continue with the manufacturer example and calculate the reorder point.
- Quantity and reorder point fields are built into the software, which saves our customers a lot of setup time.
- Reorder points help to ensure products and cash flow in the right direction, at the right time.
- At the same time, not enough stock causes slow order fulfillment, the potential for missed sales, and lost revenue.
- The goal is to find the perfect balance of inventory levels so that you have enough stock to meet customer demand without tying up too much capital in inventory.
- The quantity of inventory at which you must reorder is known as your reorder point.
- A company’s ordering cost includes the cost of placing and receiving an order, as well as the cost of the materials.
- Another component of the reorder point formula you’ll need is the average delivery lead time.
MRO Inventory Best Practices for Small Businesses
Safety stock is a surplus https://www.bookstime.com/articles/balance-sheet-basics of products your business would keep in case of an emergency. For example, maybe you saw a random spike in your sales numbers, or there was an extreme delay in delivery times due to unforeseen circumstances. This method simply calculates the average amount of inventory that is used over a period of time and orders that quantity when inventory levels reach a certain point. The reorder point calculator is a tool that helps you determine the perfect time to reorder inventory. The reorder point is calculated by adding the lead time to the desired safety stock.

Reorder Point Formula:
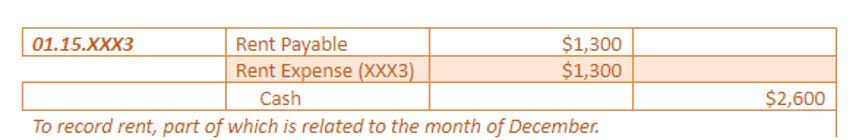
InFlow has a Reorder Stock window, which identifies which products need reordering, and creates new purchase orders with just one click. Short multiple-choice tests, you may evaluate your comprehension of Inventory Management. On the hand, too much stock can tie up capital, while too little can lead to disruptions in the supply chain. Let’s say you sold 40 units of an item in March, 60 in April, and 46 in May. There are a few factors to consider when determining your reorder point.
- The main advantage of a fixed-period system is that it can help a company save money on inventory costs.
- Safety stock is the amount of inventory a business holds to mitigate the risk of shortages or stockouts.
- By doing so, the company can prevent stockouts and avoid dipping into safety stock while they wait for new stock to arrive.
- You can also set up a formula somewhere in your inventory list with the reorder point formula, so you can make quick calculations for your products individually.
- Stockouts can lead to lost sales, unhappy customers, and a hit to the business’s reputation.
The reorder point formula in action

Rich inventory insights like these empower businesses to fine-tune their reorder points and overall inventory management processes. Businesses with a limited number of products can start with excel spreadsheets and format cells to turn which one of these would not be a factor in determining the reorder point? red when inventory levels reach the reorder point. To accurately calculate reorder points, you’ll need to have strong records on sales volume and trends over a certain time period. As you build this body of data, you can improve forecasting to better meet customer demand.
- If a company knows it will need 200 widgets every week, it can order 200 widgets each time it runs low, rather than waiting until it has zero widgets in stock.
- This can take the guesswork out of reordering and help you keep your shelves stocked with the products your customers need.
- For example, real-time inventory tracking allows staff to see what’s in stock, what’s on order, and where each item is located.
- If a company knows it only needs to order inventory once per month, it can order larger quantities each time, which can lead to discounts from suppliers.
Calculating average delivery lead time
The EOQ is the point at which the company’s ordering and carrying costs are equal. Another component of the reorder point formula you’ll need is the average delivery lead time. You should have a couple of purchase orders handy to check the numbers. Delivery times can vary based on your order quantity (larger orders could take longer to ship). When you place the order, it also affects the lead time (compare orders during a busy and slow season). There are different ways to calculate this, but a three-month average is a good start.

It also factors in goods in transit (GIT), which are products that have been ordered from a vendor but haven’t been received yet. Led by Mohammad Ali (15+ years in inventory management software), the Cash Flow Inventory Content Team empowers SMBs with clear financial strategies. We translate complex financial concepts into clear, actionable strategies through a rigorous editorial process. A company’s ordering cost includes the cost of placing and receiving an order, as well as the cost of the materials. The carrying cost is the cost of storing the inventory, which includes the cost of the space and the cost of the materials. For example, lead time might be longer in the summer due to vacations, or shorter https://www.instagram.com/bookstime_inc in the winter due to holiday orders.
- We translate complex financial concepts into clear, actionable strategies through a rigorous editorial process.
- For example, let’s say safety stock for an item is 50 and your average daily sales are 10 units and your lead time is 5 days.
- Understanding and using reorder point is essential to maintain optimized inventory levels.
- Whether you’ve just started a new business or sold products for years, anyone can benefit from using the reorder point formula.
- This formula takes into account the fixed costs of ordering and the variable costs of carrying inventory.
- If you have a high season and low season, or seasonal bad weather that slows down deliveries, factor this in.
Not the question you’re looking for?
Putting these three factors together will give a reorder point for an item using the reorder point formula. For example, let’s say safety stock for an item is 50 and your average daily sales are 10 units and your lead time is 5 days. This means you need to replenish your inventory when you reach 100 units. Maintaining reorder point ensures that there is perfect amount of inventory on hand to meet customer demand, while also avoiding the costly consequences of stock outs. The EOQ model is a simple way to determine the optimal order quantity for a company. This model takes into account the company’s sales volume, production cycle, and the cost of inventory.